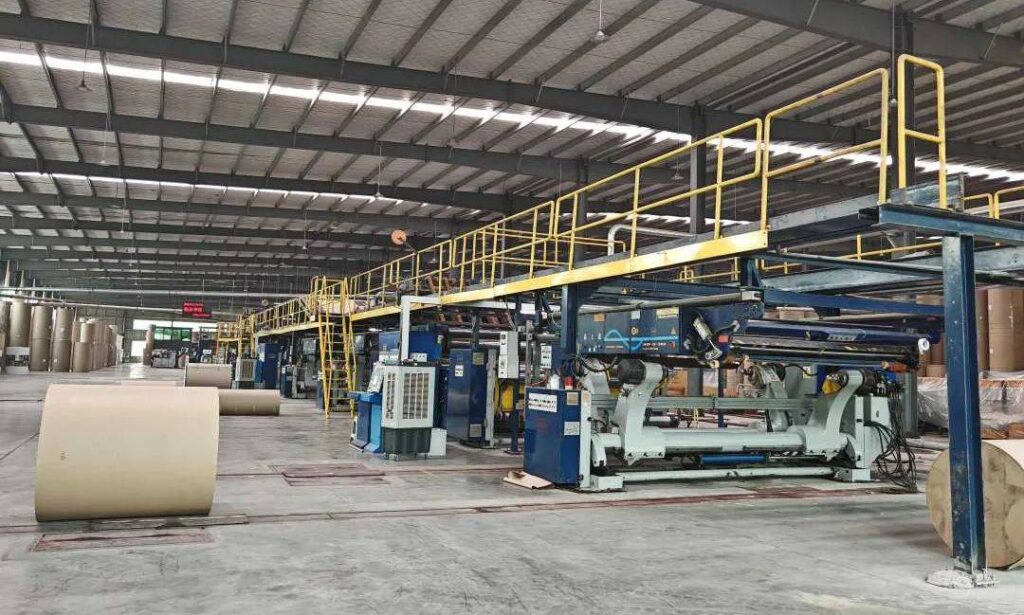
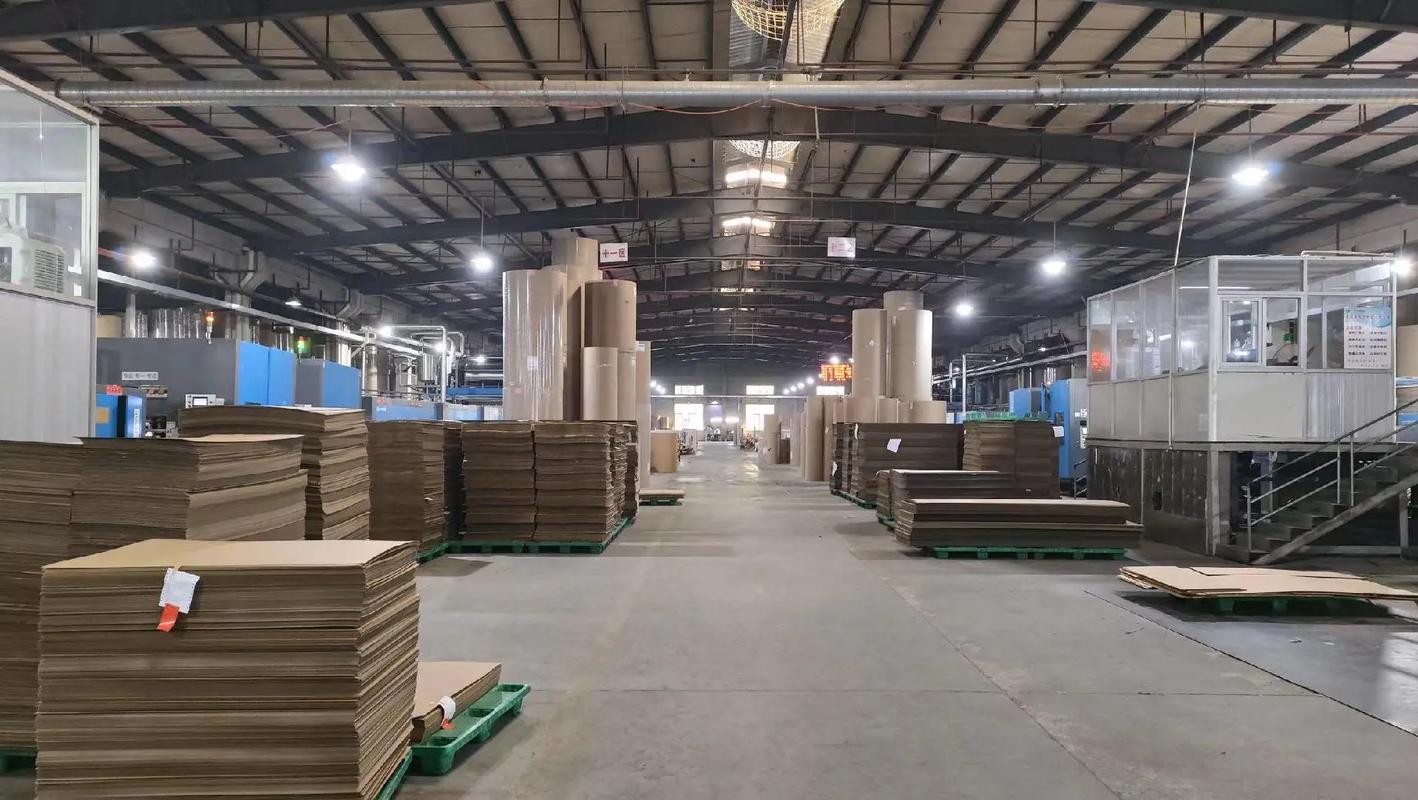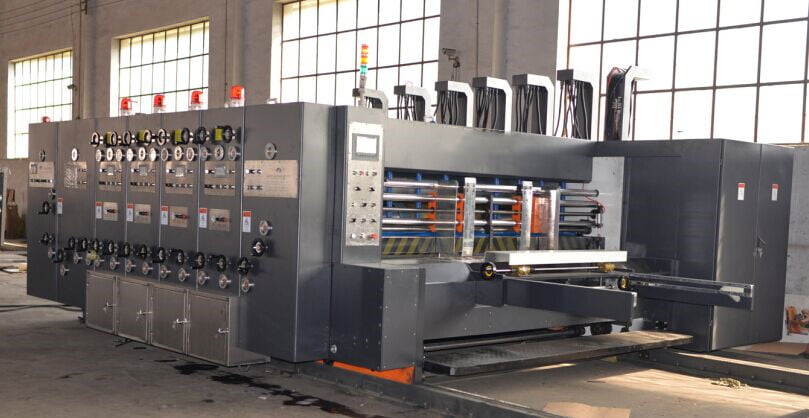
Corrugator Machine are indispensable in the production of corrugated cardboard, the backbone of modern packaging. These versatile machines are used to create durable, lightweight, and cost-effective materials that protect goods during storage and transportation.
This guide dives deep into the world of corrugated machines, covering their Main configuration, type, function, technical specifications, maintenance requirements, warranty, delivery, after-sales, and more. Whether you’re a factory owner or considering an investment in this equipment, this detailed resource will answer all your questions.
1. What is a Corrugator Machine and How Does It Work?
What is a Corrugator Machine Used For?
Corrugated machines are designed to produce corrugated cardboard, which serves as the primary material for:
- Packaging boxes: Used in industries like e-commerce, electronics, food, and beverages.
- Protective layers: Shield fragile items during transportation.
- Custom packaging: Tailored boxes for products of varying sizes and weights.
Corrugated cardboard is prized for its strength, flexibility, and cushioning properties, making it ideal for a wide range of applications.
How Does It Create Corrugated Cardboard?
The production process is multi-stage and continuous, ensuring efficiency and high output.
- Raw Material Feeding: Rolls of kraft paper are fed into the machine.
- Fluting: Heated corrugating rollers shape the paper into a wavy pattern (flutes).
- Adhesive Application: A gluing station applies adhesive to the flutes.
- Lamination: Flat linerboard layers are bonded to the fluted paper.
- Cutting and Shaping: The laminated cardboard is cut into sheets or customized shapes for further use.
Main Components of a Corrugator Machine
What Are the Main Components of the Machine?
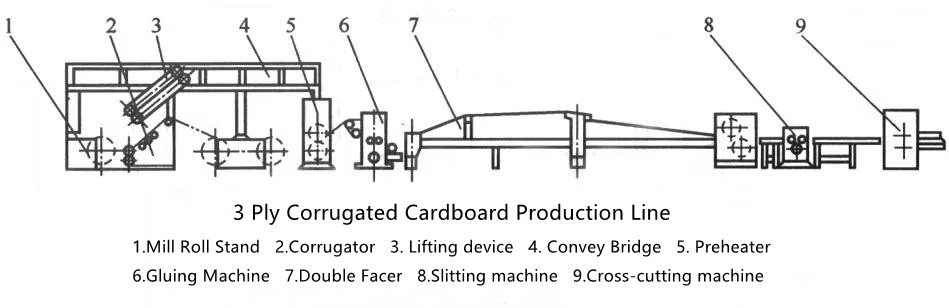
The main components of our machinery include:
- Auto Splicer: Automatically connects the ends of paper rolls to ensure continuous production without interruptions.
- Mill Roll Stand: Provides support for the incoming paper rolls, maintaining proper tension and alignment during the feeding process.
- Single Facer: Combines a single fluted medium with linerboard to create the initial corrugated structure.
- Gluing Machines: Apply adhesive to bond the fluted medium with additional linerboards, ensuring a strong and durable product.
- Double Facer: Adds another layer of linerboard to the corrugated medium, enhancing the board's strength and durability.
- Thin Blade Slitter Scorer: Cuts and scores the corrugated sheets with precision, preparing them for subsequent handling and processing.
- NC Cut Off: Utilizes numerical control technology to accurately trim the corrugated sheets to the required lengths.
- Stackers: Automatically collect and stack the finished sheets, facilitating efficient handling and storage.
- Production and Management System: Integrates software that monitors and optimizes the production process, allowing for real-time management and data analysis.
Each of these components plays a vital role in the overall performance and efficiency of our corrugated machinery, ensuring the production of high-quality corrugated products.
2. What Types of Corrugator Machines Are Available?
Types Based on Speed
| Speed Category | Features | Best Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Low-Speed | 60-100m/min; cost-effective. | Small-scale production. |
| Mid-Speed | 100-150m/min; balanced efficiency and cost. | Medium-sized factories. |
| High-Speed | 150-250m/min; fully automated. | Large-scale industrial operations. |
Types Based on Layers
| Layer Configuration | Features and Use Cases |
|---|---|
| 2-Layer | Lightweight packaging for basic needs. |
| 3-Layer | Versatile, used for most packaging products. |
| 5-Layer | Heavy-duty packaging for fragile goods. |
| 7-Layer | Maximum durability for high-value items. |
Types Based on Automation
| Automation Level | Features | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Semi-Automatic | Requires manual intervention. | Lower initial cost, good for startups. |
| Fully Automatic | Fully controlled by intelligent systems. | High efficiency, minimal labor cost. |
How to Choose the Right Machine?
Choosing the right corrugator machines is essential to ensure efficient production and meet your business needs. Here are the key factors to consider:
1. Understand Production Needs
- Product Type: Identify the type of products you plan to manufacture (e.g., corrugated sheets, boxes, or inserts).
- Production Volume: Estimate your daily, weekly, and monthly production requirements. Consider whether there may be an increase in production volume in the future.
- Customization Requirements: If specific product sizes, shapes, or printing designs are needed, select machines that support these features.
2. Machine Quality and Performance
- Stability: High-quality machines with stable performance reduce downtime and maintenance costs, ensuring consistent production.
- Precision: Machines with excellent cutting and bonding accuracy improve product quality and minimize material waste.
- Durability: Opt for robust machines with long service life to maximize your return on investment.
3. Machine Specifications
- Speed: Ensure the machine’s speed (e.g., sheets or meters per minute) aligns with your current and future production needs.
- Layers: Choose machines suitable for producing single-wall, double-wall, or multi-wall corrugated boards, depending on your product requirements.
- Automation Level: Select fully automatic, semi-automatic, or manual machines based on your budget and labor availability.
4. Space and Facility Requirements
- Factory Space: Ensure sufficient room for machines, material storage, and smooth workflow.
- Power Supply: Verify that your facility meets the power requirements of the machine.
- Environmental Conditions: Consider ventilation, humidity, and temperature requirements for optimal machine operation.
5. Budget and Cost Analysis
- Initial Cost: Assess the upfront cost of the machine, including taxes and delivery.
- Operating Cost: Consider energy consumption, labor requirements, and daily maintenance expenses.
- Return on Investment (ROI): Calculate the time needed to recover your investment and ensure it is reasonable.
6. Supplier and After-Sales Service
- Reputation: Choose a reliable supplier with good reviews and proven experience in the industry.
- Technical Support: Ensure the supplier provides technical training, equipment installation, and spare parts.
- Warranty: Understand the warranty period and what it covers.
7. Compliance and Certification
- Safety Standards: Ensure the machine complies with local safety standards.
- Quality Certifications: Look for certifications like ISO or CE to ensure product quality and reliability.
8. Machine Demonstration and Testing
- Performance Check: Request a live demonstration or test run to evaluate the machine’s performance and ease of operation.
- Product Quality: Inspect the quality of finished products during the test to ensure they meet your requirements.
9. Flexibility and Future Growth
- Versatility: Choose machines capable of handling diverse products to meet different order requirements.
- Support for Expansion: Plan for business growth and ensure the machine can meet increased production demands.
By carefully analyzing these factors, you can select a corrugated machine that meets your current needs, supports your future growth, and maximizes your production efficiency and long-term benefits.
3. Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness of Corrugator Machines
Energy Consumption example
| Layers | Speed (m/min) | Energy (kWh/hour) | Steam (kg/hour) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1800mm-3-Layer | 120-130 | 130-160 | 1500-1700 |
| 2500mm-5-Layer | 150 | 250-320 | 4500-5500 |
Operating Costs
The operating costs of a corrugated machine include energy consumption, labor, maintenance, and raw materials. Here's a breakdown of typical costs:
- Electricity: Energy costs can range from 120-350 kWh per hour depending on the machine's configuration.
- Steam: Corrugators typically consume 1500-7000 kg of steam per hour, with the cost depending on local energy prices.
- Labor:Automated machines reduce the need for manual labor, especially in high-speed lines. Labor costs may still be necessary for machine setup, maintenance, and supervision.
-Maintenance:Routine maintenance, including lubrication, part replacements, and adjustments, is essential to ensure smooth operations. These costs can range from $5,000 to $20,000 per year, depending on machine size and usage.
ROI and Cost Efficiency
- ROI Period: Typically 2-5 years depending on scale.
- Strategies to improve ROI:
Reducing energy consumption is crucial for improving the cost-effectiveness of a corrugator line. Here are several strategies to help minimize energy usage:
1.Optimize Production Scheduling:
Arrange production runs with similar paper quality and sizes to reduce waste and minimize the number of times paper rolls need to be changed. This reduces energy spent on paper transitions and ensures smooth machine operation.
2.Minimize Material Waste:
Carefully calculate the cardboard area to ensure optimal use of raw materials and reduce unnecessary waste. Scheduling the production of cartons of similar sizes and qualities together can reduce material wastage and improve efficiency.
3.Regular Maintenance:
Keeping the machine well-maintained ensures that all components function efficiently, preventing energy waste. Regular maintenance, such as proper lubrication of bearings and ensuring the steam system is leak-free, helps reduce energy losses.
4.Implement Automation:
Use automatic paper splicers to reduce paper waste and speed up the production process. This improves efficiency and reduces the need for manual intervention, lowering energy consumption.
5.Energy-Efficient Technology:
Some modern corrugators come equipped with energy-saving features like optimized motors, energy recovery systems, and intelligent control systems that adjust operations based on paper quality and vehicle speed. This ensures that energy usage is always aligned with production demands.
6.Use Energy Monitoring Systems:
Implementing an energy management system that tracks energy usage in real time can help identify areas where energy can be saved, improving overall operational efficiency.
4. Maintenance Requirements and Lifespan
Regular maintenance ensures the efficient operation and longevity of corrugated machines. Below is a detailed breakdown of maintenance schedules and tasks.

Maintenance Schedule
1. Daily Maintenance
Daily maintenance tasks focus on cleaning, lubrication, and operational checks to ensure smooth performance:
- Cleaning Tasks
- Equipment Surface Cleaning: After each production shift, wipe down equipment surfaces to remove dust, paper scraps, and glue residues. Ensure key parts, such as corrugated and pressure rollers, are free from foreign substances.
- Conveyor Belt Cleaning: Remove paper scraps and glue residue promptly to prevent misalignment, which can affect board accuracy.
- Lubrication Tasks
- Check Lubrication Points: Refer to the equipment manual to identify and inspect lubrication points (e.g., gears, chains, bearings) daily to ensure sufficient oil levels.
- Use Suitable Lubricants: Select lubricants based on component requirements (e.g., high-temperature grease for heating components, low-viscosity oil for high-speed gears).
- Operational Checks
- Monitor Sounds: Ensure smooth operation without abnormal noises. Any friction or impact sounds require immediate inspection.
- Check Speed and Temperature: Verify that the machine operates at the required speed and within normal temperature ranges. Overheating motors or heating devices may indicate malfunctions needing prompt attention.
2. Regular Maintenance (Weekly or Monthly)
These tasks address wear and tear, ensuring machine components remain aligned and functional:
- Mechanical Checks and Adjustments
- Tighten Bolts and Nuts: Inspect bolts, especially on parts subjected to vibration (e.g., corrugated roller fixtures, drive chains).
- Conveyor Belt Tension: Use a tension meter to maintain proper belt tension. High tension shortens belt lifespan, while low tension may cause slipping.
- Roller Wear and Alignment: Inspect corrugated and pressure rollers for wear. Regrind or replace worn rollers, and verify their parallelism and concentricity.
- Electrical System Maintenance
- Control Panel Cleaning: Use compressed air or a soft brush to remove dust from control panels to prevent overheating or short circuits.
- Check Electrical Connections: Ensure wiring, contactors, and relays are secure. Look for signs of discoloration or overheating.
- Software Updates and Backups: Update automated system software regularly to fix bugs and add features. Backup programs to prevent data loss.
3. Long-Term Maintenance (Every Six Months or Annually)
Comprehensive maintenance ensures long-term stability and identifies potential issues early:
- Consumables Check and Replacement
- Inventory Management: Maintain a list of consumables (e.g., corrugated rollers, conveyor belts, cutters) and check wear levels.
- Replacement Plan: Replace rollers when corrugation height exceeds limits. Schedule replacements to prevent production delays.
- Calibration and Performance Testing
- Calibrate Precision: Use tools like laser range finders to verify key parts’ alignment and accuracy (e.g., rollers’ parallelism and concentricity).
- Performance Testing: Produce test batches to measure board thickness, flute quality, and strength, comparing results to design parameters.
Key Parts of the Corrugated Machine and Their Maintenance
| Component | Maintenance Task | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Corrugated Rollers | Clean weekly; inspect for wear every 1-2 weeks; replace as needed to maintain corrugation quality. | Weekly/Bi-weekly |
| Pressure Rollers | Adjust pressure based on paper type; inspect and clean monthly to maintain bonding strength. | Monthly |
| Heating System | Check for steam leaks, inspect boilers, and clean temperature controls to ensure even heating. | Quarterly |
| Conveyor System | Inspect belts for damage; adjust tension and clean comprehensively every 3-6 months. | Every 3-6 months |
| Gluing System | Clean glue rollers daily; ensure circulation system is free from blockages. | Daily/As needed |
Expected Lifespan of Key Components
- Main Frame: 10-15 years with proper maintenance.
- Corrugated Rollers: 2-5 years, depending on usage intensity and material quality.
- Pressure Rollers: 3-6 years with regular care.
- Heating System: Steam systems last 10-15 years; electric heating elements last 3-5 years.
- Conveyor Belts: 3-5 years, depending on operating conditions.
By adhering to this maintenance schedule, you can maximize the performance and longevity of your corrugated machine, ensuring consistent production quality and reducing unexpected downtime.
5. Technical Specifications
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Max Production Speed | Up to 250 m/min |
| Width Options | 1.4-2.8m |
| Paper Grammage Range | 80-300 g/m² |
| Automation Features | Tension control, remote diagnostics, auto stacking. |
6. Cost of Corrugated Machines
| Machine Type | Price Range (USD) |
|---|---|
| Small-Scale | $100,000 - $300,000 |
| Medium-Scale | $500,000 - $1,000,000 |
| Large-Scale | $1,000,000 and above |
Factors Influencing Cost:
- Production Capacity: Higher speeds and widths cost more.
- Automation: Fully automated machines are pricier upfront but save in the long run.
7. Reliability and Warranty
Reliability
The reliability of corrugated cardboard production line machines is determined by their design, manufacturing quality, and maintenance. Below are the key aspects:
1. Design and Manufacturing
- Machines are designed by experienced teams using advanced technologies and mature processes.
- High-strength, wear-resistant materials are used for key components, such as corrugating rollers and heating plates, ensuring long-term stability and durability.

2. Quality Control
- Manufacturers conduct strict quality control throughout the production process:
- Raw Material Inspection: Ensures only high-quality materials are used.
- Machining Accuracy: Precision-controlled during parts manufacturing.
- Assembly Quality: Checked using non-destructive testing and performance testing.
- These processes ensure machines meet high standards and deliver consistent reliability.
3. Automation and Intelligence
- Modern machines integrate intelligent control systems that:
- Monitor machine performance in real time.
- Automatically adjust parameters to reduce human error.
- Improve production consistency and stability.
- Offer fault diagnosis and early warning features to address issues promptly.
4. Maintenance
- Regular maintenance is essential to sustaining machine reliability.
- Key maintenance practices include:
- Cleaning, lubricating, and tightening components.
- Timely replacement of worn parts.
- Adherence to proper operating procedures to extend service life.
Warranty Options
Manufacturers typically provide a 1 to 2-year warranty for corrugated cardboard production line machines. The exact warranty terms may vary based on product characteristics, quality assurance strategies, and customer needs.
Warranty Coverage
- Replacement of Parts
- Free replacement of parts damaged due to quality issues during the warranty period.
- Maintenance Services
- Professional technicians are dispatched for inspection and troubleshooting at no additional cost.
- Technical Support
- Comprehensive support, including operation guidance and parameter adjustments, is offered to resolve technical challenges.
Customer Support
Reliable customer support is vital to ensuring smooth operation and minimal downtime.
1. Hotline Service
- A dedicated customer service hotline allows users to contact technical support quickly for immediate assistance.
2. On-Site Service
- When remote troubleshooting is insufficient, manufacturers send professional technicians to the site for:
- Repairs and debugging.
- Ensuring timely resumption of normal operations.
3. Training Services
- Manufacturers offer training for operators and maintenance personnel, covering:
- Equipment operation methods.
- Maintenance best practices.
- Common troubleshooting techniques.
4. Spare Parts Handling
| Service | Details |
|---|---|
| Spare Parts Supply | Manufacturers maintain an inventory system for timely delivery of parts. |
| Original Spare Parts | Ensure better compatibility and quality by using manufacturer-provided parts. |
| Emergency Spare Parts | Expedited delivery services for urgent situations to minimize downtime. |
By focusing on design, quality, automation, maintenance, and comprehensive customer support, corrugated machine manufacturers ensure long-term reliability and customer satisfaction.
8. Lead Time for Delivery and Installation
Efficient delivery and professional installation are critical to ensuring the smooth operation of your corrugated machine. Below is a detailed breakdown:
Delivery and Installation Timeline
- Production and Delivery: Typically takes 4-6 months to manufacture and deliver the equipment.
- Installation Time: Generally 1-3 months, which includes on-site setup and operator training.
- Shipping: Machines are shipped with moisture-proof packaging and real-time tracking for safe and timely delivery.
International Installation Process
- Installation Team Dispatch
- A team of experienced and professional installation engineers will be sent to the customer’s location upon request.
- Engineers have extensive knowledge of equipment operation and installation procedures, ensuring efficient setup.
- On-Site Coordination
- Upon arrival, the installation team will:
- Communicate with the customer to understand local construction conditions and safety regulations.
- Coordinate resources such as installation sites, personnel, and necessary tools.
- Upon arrival, the installation team will:
- Installation and Training
- Engineers will install and debug the equipment in accordance with the installation manual and operating procedures, ensuring the equipment operates stably.
- On-site training for the customer’s operators and maintenance personnel will include:
- Equipment operation methods.
- Maintenance best practices.
- Troubleshooting common issues.
Charges for Transportation and Installation
Costs for transportation and installation are calculated based on several factors:
- Transportation Costs
- Include sea freight and insurance charges.
- Final cost depends on:
- Volume and weight of the equipment.
- Box type, shipping destination (country/port), and shipping season.
- Installation Costs
- If on-site installation is requested, customers are responsible for:
- Visa fees for the installation engineers.
- Round-trip airfare.
- Accommodation during the installation period.
- Engineer’s salary for the duration of the installation.
- If on-site installation is requested, customers are responsible for:
By providing a clear delivery and installation process, along with transparent cost structures, we aim to ensure a seamless experience for our customers while maintaining high-quality service standards.
9. After-Sales Services
| Service | Details |
|---|---|
| Training | Operator and maintenance training available. |
| Technical Support | Remote monitoring and on-site assistance. |
| Spare Parts Supply | Extensive inventory for fast delivery. |
10. Customization Options
Common Customizations
- Machine width, speed, and layer options.
- Special features like preprinting, moisture-proofing, and custom flute profiles.
Optional Accessories
- High-precision glue rollers.
- Advanced automation for real-time monitoring.
Conclusion
Corrugated machines are the foundation of efficient and scalable packaging production. Investing in the right type, maintaining it well, and leveraging advanced features will ensure long-term success. For tailored solutions, contact us today.




